篇首语:本文由编程笔记#小编为大家整理,主要介绍了YYDS!Python实现自动驾驶相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
gym是用于开发和比较强化学习算法的工具包,在python中安装gym库和其中子场景都较为简便。
安装gym:
pip install gym
安装自动驾驶模块,这里使用Edouard Leurent发布在github上的包highway-env(链接:https://github.com/eleurent/highway-env):
pip install --user git+https://github.com/eleurent/highway-env
其中包含6个场景:
高速公路——“highway-v0”
汇入——“merge-v0”
环岛——“roundabout-v0”
泊车——“parking-v0”
十字路口——“intersection-v0”
赛车道——“racetrack-v0”
详细文档可以参考这里:
https://highway-env.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
安装好后即可在代码中进行实验(以高速公路场景为例):
import gym
import highway_env
%matplotlib inline
env = gym.make('highway-v0')
env.reset()
for _ in range(3):
action = env.action_type.actions_indexes["IDLE"]
obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
运行后会在模拟器中生成如下场景:
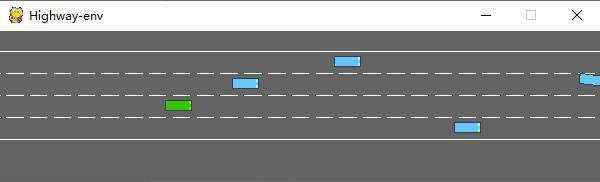
绿色为ego vehicle env类有很多参数可以配置,具体可以参考原文档。
highway-env包中没有定义传感器,车辆所有的state (observations) 都从底层代码读取,节省了许多前期的工作量。根据文档介绍,state (ovservations) 有三种输出方式:Kinematics,Grayscale Image和Occupancy grid。
Kinematics
输出V*F的矩阵,V代表需要观测的车辆数量(包括ego vehicle本身),F代表需要统计的特征数量。例:
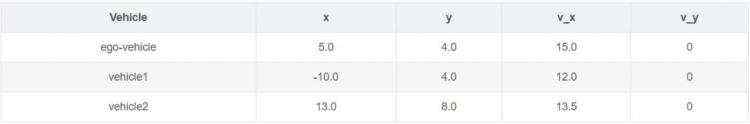
数据生成时会默认归一化,取值范围:[100, 100, 20, 20],也可以设置ego vehicle以外的车辆属性是地图的绝对坐标还是对ego vehicle的相对坐标。
在定义环境时需要对特征的参数进行设定:
config = \\
"observation":
"type": "Kinematics",
#选取5辆车进行观察(包括ego vehicle)
"vehicles_count": 5,
#共7个特征
"features": ["presence", "x", "y", "vx", "vy", "cos_h", "sin_h"],
"features_range":
"x": [-100, 100],
"y": [-100, 100],
"vx": [-20, 20],
"vy": [-20, 20]
,
"absolute": False,
"order": "sorted"
,
"simulation_frequency": 8, # [Hz]
"policy_frequency": 2, # [Hz]
Grayscale Image
生成一张W*H的灰度图像,W代表图像宽度,H代表图像高度
Occupancy grid
生成一个WHF的三维矩阵,用W*H的表格表示ego vehicle周围的车辆情况,每个格子包含F个特征。
highway-env包中的action分为连续和离散两种。连续型action可以直接定义throttle和steering angle的值,离散型包含5个meta actions:
ACTIONS_ALL =
0: 'LANE_LEFT',
1: 'IDLE',
2: 'LANE_RIGHT',
3: 'FASTER',
4: 'SLOWER'
highway-env包中除了泊车场景外都采用同一个reward function:
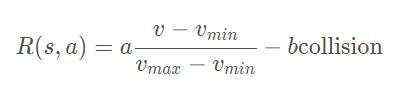
这个function只能在其源码中更改,在外层只能调整权重。(泊车场景的reward function原文档里有,懒得打公式了……)
DQN网络的结构和搭建过程已经在我另一篇文章中讨论过,所以这里不再详细解释。我采用第一种state表示方式——Kinematics进行示范。
由于state数据量较小(5辆车*7个特征),可以不考虑使用CNN,直接把二维数据的size[5,7]转成[1,35]即可,模型的输入就是35,输出是离散action数量,共5个。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torchvision.transforms as T
from torch import FloatTensor, LongTensor, ByteTensor
from collections import namedtuple
import random
Tensor = FloatTensor
EPSILON = 0 # epsilon used for epsilon greedy approach
GAMMA = 0.9
TARGET_NETWORK_REPLACE_FREQ = 40 # How frequently target netowrk updates
MEMORY_CAPACITY = 100
BATCH_SIZE = 80
LR = 0.01 # learning rate
class DQNNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DQNNet,self).__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(35,35)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(35,5)
def forward(self,s):
s=torch.FloatTensor(s)
s = s.view(s.size(0),1,35)
s = self.linear1(s)
s = self.linear2(s)
return s
class DQN(object):
def __init__(self):
self.net,self.target_net = DQNNet(),DQNNet()
self.learn_step_counter = 0
self.memory = []
self.position = 0
self.capacity = MEMORY_CAPACITY
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.net.parameters(), lr=LR)
self.loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
def choose_action(self,s,e):
x=np.expand_dims(s, axis=0)
if np.random.uniform() < 1-e:
actions_value &#61; self.net.forward(x)
action &#61; torch.max(actions_value,-1)[1].data.numpy()
action &#61; action.max()
else:
action &#61; np.random.randint(0, 5)
return action
def push_memory(self, s, a, r, s_):
if len(self.memory) < self.capacity:
self.memory.append(None)
self.memory[self.position] &#61; Transition(torch.unsqueeze(torch.FloatTensor(s), 0),torch.unsqueeze(torch.FloatTensor(s_), 0),\\
torch.from_numpy(np.array([a])),torch.from_numpy(np.array([r],dtype&#61;&#39;float32&#39;)))#
self.position &#61; (self.position &#43; 1) % self.capacity
def get_sample(self,batch_size):
sample &#61; random.sample(self.memory,batch_size)
return sample
def learn(self):
if self.learn_step_counter % TARGET_NETWORK_REPLACE_FREQ &#61;&#61; 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.net.state_dict())
self.learn_step_counter &#43;&#61; 1
transitions &#61; self.get_sample(BATCH_SIZE)
batch &#61; Transition(*zip(*transitions))
b_s &#61; Variable(torch.cat(batch.state))
b_s_ &#61; Variable(torch.cat(batch.next_state))
b_a &#61; Variable(torch.cat(batch.action))
b_r &#61; Variable(torch.cat(batch.reward))
q_eval &#61; self.net.forward(b_s).squeeze(1).gather(1,b_a.unsqueeze(1).to(torch.int64))
q_next &#61; self.target_net.forward(b_s_).detach() #
q_target &#61; b_r &#43; GAMMA * q_next.squeeze(1).max(1)[0].view(BATCH_SIZE, 1).t()
loss &#61; self.loss_func(q_eval, q_target.t())
self.optimizer.zero_grad() # reset the gradient to zero
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step() # execute back propagation for one step
return loss
Transition &#61; namedtuple(&#39;Transition&#39;,(&#39;state&#39;, &#39;next_state&#39;,&#39;action&#39;, &#39;reward&#39;))
各个部分都完成之后就可以组合在一起训练模型了&#xff0c;流程和用CARLA差不多&#xff0c;就不细说了。
初始化环境&#xff08;DQN的类加进去就行了&#xff09;&#xff1a;
import gym
import highway_env
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import time
config &#61; \\
"observation":
"type": "Kinematics",
"vehicles_count": 5,
"features": ["presence", "x", "y", "vx", "vy", "cos_h", "sin_h"],
"features_range":
"x": [-100, 100],
"y": [-100, 100],
"vx": [-20, 20],
"vy": [-20, 20]
,
"absolute": False,
"order": "sorted"
,
"simulation_frequency": 8, # [Hz]
"policy_frequency": 2, # [Hz]
env &#61; gym.make("highway-v0")
env.configure(config)
训练模型&#xff1a;
dqn&#61;DQN()
count&#61;0
reward&#61;[]
avg_reward&#61;0
all_reward&#61;[]
time_&#61;[]
all_time&#61;[]
collision_his&#61;[]
all_collision&#61;[]
while True:
done &#61; False
start_time&#61;time.time()
s &#61; env.reset()
while not done:
e &#61; np.exp(-count/300) #随机选择action的概率&#xff0c;随着训练次数增多逐渐降低
a &#61; dqn.choose_action(s,e)
s_, r, done, info &#61; env.step(a)
env.render()
dqn.push_memory(s, a, r, s_)
if ((dqn.position !&#61;0)&(dqn.position % 99&#61;&#61;0)):
loss_&#61;dqn.learn()
count&#43;&#61;1
print(&#39;trained times:&#39;,count)
if (count%40&#61;&#61;0):
avg_reward&#61;np.mean(reward)
avg_time&#61;np.mean(time_)
collision_rate&#61;np.mean(collision_his)
all_reward.append(avg_reward)
all_time.append(avg_time)
all_collision.append(collision_rate)
plt.plot(all_reward)
plt.show()
plt.plot(all_time)
plt.show()
plt.plot(all_collision)
plt.show()
reward&#61;[]
time_&#61;[]
collision_his&#61;[]
s &#61; s_
reward.append(r)
end_time&#61;time.time()
episode_time&#61;end_time-start_time
time_.append(episode_time)
is_collision&#61;1 if info[&#39;crashed&#39;]&#61;&#61;True else 0
collision_his.append(is_collision)
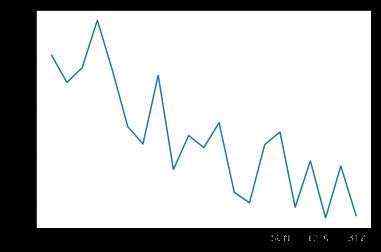
我在代码中添加了一些画图的函数&#xff0c;在运行过程中就可以掌握一些关键的指标&#xff0c;每训练40次统计一次平均值。
平均碰撞发生率&#xff1a;
epoch平均时长(s)&#xff1a;
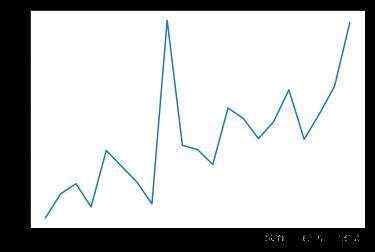
平均reward&#xff1a;

可以看出平均碰撞发生率会随训练次数增多逐渐降低&#xff0c;每个epoch持续的时间会逐渐延长&#xff08;如果发生碰撞epoch会立刻结束&#xff09;
相比于我在之前文章中使用过的模拟器CARLA&#xff0c;highway-env环境包明显更加抽象化&#xff0c;用类似游戏的表示方式&#xff0c;使得算法可以在一个理想的虚拟环境中得到训练&#xff0c;而不用考虑数据获取方式、传感器精度、运算时长等现实问题。对于端到端的算法设计和测试非常友好&#xff0c;但从自动控制的角度来看&#xff0c;可以入手的方面较少&#xff0c;研究起来不太灵活。
推荐阅读 点击标题可跳转
Python 学习手册
Pandas 学习大礼包
100&#43; Python 爬虫项目
100 道 Python 经典练习题
Python 数据分析入门手册
2022最强Python学习神器来了
70 个 Python 经典实用练手项目
20张高清数据分析(Python)全知识地图
14 张 Python 速查表玩转数据分析&机器学习


 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有